- Home
- Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar Cancer
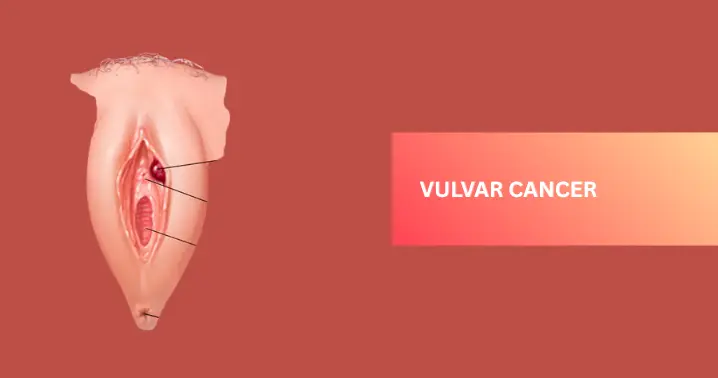
Vulvar Cancer is a rare type of gynecological cancer that affects the external female genital organs, most commonly the labia. It accounts for about 4–5% of all gynecologic cancers globally.
While it is more frequently diagnosed in older women, cases in younger women have been rising due to factors such as HPV infection and weakened immunity.
The disease burden is higher in regions with limited access to regular gynecological check-ups and cancer screening programs.
However, with early detection, HPV vaccination, and advanced treatment options — including expert vulvar cancer treatment in Ahmedabad — the chances of successful recovery and long-term survival can be significantly improved.
What is Vulvar Cancer?
Vulvar cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops on the outer surface of the female genital organs, known as the vulva. It most commonly affects the labia majora or labia minora but can also involve the clitoris or vaginal opening. This cancer typically begins as abnormal cells on the skin of the vulva, which may grow slowly over time and develop into malignancy. Vulvar cancer is more commonly diagnosed in older women, but younger women can also be affected, especially those with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection or weakened immune systems.
There are different types of vulvar cancer, with squamous cell carcinoma being the most common. Symptoms may include itching, burning, pain, a lump, ulcer, or bleeding on the vulva that doesn’t heal. Early detection through regular gynecological exams can lead to better treatment outcomes. Treatment options often include surgery, radiation therapy, and in some cases, chemotherapy, depending on the stage and type of cancer.
Signs and Symptoms of Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer often begins with subtle signs that can be mistaken for minor infections or skin conditions. Symptoms like persistent itching, visible sores, or unusual lumps should not be ignored, especially if they do not heal over time. Early detection of these warning signs is crucial, as vulvar cancer is highly treatable in its early stages with proper medical intervention.
- Persistent itching or burning in the vulvar area
- A lump, bump, or sore that doesn’t heal
- Pain or tenderness in the vulva
- Unusual bleeding or discharge not related to menstruation
- Changes in the color or thickness of the vulvar skin
- Wart-like growths or open ulcers
- Pain during urination or sexual intercourse
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area
Causes of Vulvar Cancer
1. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection:
A long-term infection with high-risk HPV types increases the risk of vulvar cell changes and cancer.
2. Increasing Age:
Vulvar cancer is more common in women over 60, as aging weakens immune surveillance and tissue resistance.
3. Smoking:
Tobacco use lowers immunity and damages vulvar cells, making them more vulnerable to cancer development.
4. Weakened Immune System
Conditions like HIV or long-term immunosuppressive therapy reduce the body’s ability to fight HPV infections.
5. Chronic Vulvar Skin Conditions
Disorders like lichen sclerosus can cause long-term irritation and increase the risk of vulvar cancer.
6. Previous History of Cervical or Vaginal Cancer
A history of other gynecologic cancers or precancers may elevate the chance of vulvar cancer.
7. Persistent Vulvar Inflammation or Irritation
Chronic itching, infections, or skin trauma may cause abnormal cellular changes in the vulva.
If You Notice Any of These Symptoms
Diagnosis of Vulvar Cancer
1.Physical Examination
– Doctor checks the vulva for visible changes
– Looks for lumps, sores, or skin discoloration
2. Pelvic Examination
– Internal reproductive organs are assessed
– Helps detect any spread to nearby areas
3. Biopsy
– Small tissue sample taken from suspicious area
– Confirms presence and type of cancer
4. Colposcopy
– Magnified view of vulva using a colposcope
– Identifies abnormal or pre-cancerous cells
5. Imaging Tests (MRI/CT Scan)
– Determines the size and spread of cancer
– Helps in staging and treatment planning
6. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
– Checks if cancer has spread to lymph nodes
– Guides surgical and radiation decisions
Treatments for Vulvar Cancer in Ahmedabad
Surgery
Surgery is the most common and effective treatment for early-stage vulvar cancer.
Wide Local Excision – Removal of cancerous tissue with a margin of healthy skin.
Vulvectomy – Partial or complete removal of the vulva depending on the cancer’s extent.
Lymph Node Dissection – Removal of lymph nodes in the groin to check for cancer spread.
Radiation therapy
Used before or after surgery to shrink tumors or kill remaining cancer cells.
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) – Targets the tumor and surrounding tissue.
Often combined with chemotherapy in advanced cases.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be used in advanced stages or when cancer has spread.
Helps shrink tumors before surgery or enhance the effects of radiation therapy.
Given in cycles through IV or oral medication.
Targeted Therapy & Immunotherapy
Emerging treatment options for advanced or recurrent vulvar cancer.
Target specific cancer cells without harming healthy tissue.
May be considered for cases resistant to standard treatment.
Reconstructive Surgery & Supportive Care
Post-surgical reconstruction may be needed in extensive surgeries.
Conclusion
Vulvar cancer is rare but highly treatable when detected early. Regular screenings and awareness of risk factors can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.

Why Dr. Ridham Shah
A Surgical Oncologist Practicing In The City Of Ahmedabad
- Experience of a decade in treating cancer
- Expertise in Laparoscopic cancer surgery, Robotic cancer surgery
- Expertise in Digestive System Cancers, Colorectal cancers , Peritoneal cancers, advanced abdominal cancers
- Expertise in Cytoreductive Surgery, HIPEC, PIPAC
- Excellent support staff to help you during treatment
- 360 degree care
Specialities

Ovary Cancer

Rectal Cancer

Colon Cancer

Endometrial Cancer

Liver Cancer

Esophageal Cancer

HIPEC Surgery

Robotic Surgery

Vulvar Cancer

Gallbladder Cancer

Stomach Cancer

Pancreatic Cancer

Cervix Cancer
