- Home
- Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian Cancer Specialist Ahmedabad is a serious condition that begins in the ovaries and often develops silently, with symptoms that are easy to overlook in the early stages. It commonly affects women over 40, and warning signs may include bloating, pelvic pain, and changes in appetite or urinary habits. Because these symptoms are often mistaken for less serious issues, early detection becomes a challenge.
Dr. Ridham Shah specializes in diagnosing and treating ovarian cancer with a personalized and compassionate approach. He focuses on identifying the disease at an early stage through advanced screening methods, especially for women with a family history or genetic risk. His commitment to timely intervention and patient-centered care ensures that each individual receives the best possible outcome on their path to recovery.
What is Ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a severe health issue that originates in the ovaries, the female reproductive glands. It is often undetected until advanced stages due to subtle symptoms like bloating, pelvic pain, or frequent urination, it can be challenging to treat. Risk factors include age, inherited gene mutations, family history of ovarian cancer, and endometriosis.
However, if caught early, ovarian cancer is highly treatable and associated with long-term survival. Regular screenings and awareness about this condition are crucial for early detection and successful treatment. Trust your oncologist for guidance and care in this health journey.
Types of Ovarian Cancer
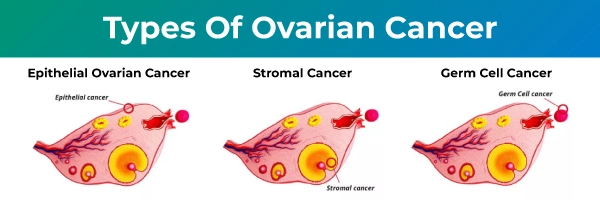
Ovarian cancer, a serious health concern in women, is categorized into three primary types based on the cells where it originates.
1. Epithelial ovarian cancer: This is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of cases. It begins in the thin layer of tissue covering the outer side of the ovaries.
2. Stromal ovarian cancer: Making up about 7% of cases, this type starts in the ovarian tissue that contains hormone-producing cells.
3. Germ cell ovarian cancer: Rare but most common in younger women, it begins in the egg-producing cells.
Each type presents unique challenges and requires different treatment approaches. Symptoms are often subtle and can include bloating, pelvic pain, and frequent urination. Regardless of the type, early detection significantly enhances treatment success. Consulting an Ovarian Cancer Specialist Ahmedabad can help with timely diagnosis. Regular screenings and understanding these types can support early diagnosis and more effective treatment strategies.
Signs and symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
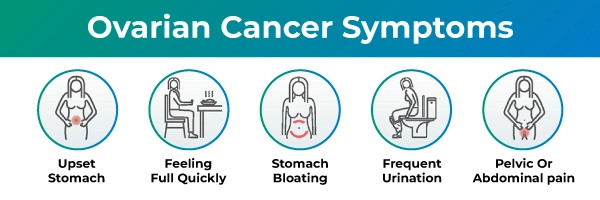
Ovarian cancer often presents subtle signs and symptoms in its early stages, making it challenging to diagnose. However, early recognition of these indications can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment.
Key symptoms include:
1.Persistent bloating or abdominal swelling: This symptom is not transient and may be a signal of ovarian cancer.
2. Pelvic or abdominal discomfort or pain: Continuous pain in these regions could be a red flag.
3. Early satiety or difficulty eating: If you’re quickly feeling full or have trouble eating, it might indicate a problem.
4. Frequent urination: An abrupt increase in urination frequency without an increase in fluid intake could be a symptom.
5. Changes in bowel movements: Symptoms such as constipation or other bowel changes may be related to ovarian cancer.
6. Unexplained weight loss: Rapid weight loss without targeted efforts might be a sign.
Always consult an oncologist if these symptoms persist or cause concern.
If You Notice Any of These Symptoms
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
Diagnosis of ovarian cancer typically involves several steps, given its subtle symptoms that often mimic other conditions.
1. Physical examination: The oncologist may palpate the abdomen and pelvis for masses or fluid build-up. A pelvic exam may also be done to check for abnormalities in the ovaries.
2. Imaging tests: Ultrasounds, CT/PET scans, or MRI may be used to identify ovarian tumors and determine their size and spread.
3. Blood tests: CA-125 is a protein elevated in many women with ovarian cancer. Blood tests checking for this marker can aid diagnosis, although it’s not definitive as other conditions can also raise CA-125 levels. Sometimes, especially in premenopausal females, other blood markers like HE-4, ROMA index are used to estimate the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. AFP levels, LDH levels and b-HCG levels are routinely measured in premenopausal young females where germ cell tumors are more common.
4.Biopsy: A definitive diagnosis requires a biopsy. This involves removing tissue or fluid from the suspected area and examining it under a microscope for cancer cells. However, in early stage ovarian cancer biopsy is not performed for the fear of tumor spillage and upstaging of the disease.
5. Laparoscopy or laparotomy: Laparsocopy helps in determining the extent of disease spread by visual examination.This is turn helps in planning a treatment strategy ( for e.g. Chemotherapy first Vs.Surgery first approach ).
Laparoscopy also helps in taking biopsies from suitable areas.In suspected early stage ovarian cancer, a direct surgery without tissue diagnosis is advisable. Here the surgery works both as a diagnostic and as a therapeutic modality. The aim of such surgery is removal of all the visible tumour nodules.
6. Staging: If cancer is confirmed, further tests are done to determine its stage and spread.
Remember, early detection improves treatment success. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult an oncologist promptly.
Test for Ovarian Cancer
Testing for ovarian cancer involves a series of examinations and procedures, usually guided by an experienced ovarian cancer specialist in Ahmedabad. The process begins with a pelvic exam to check for any abnormalities in the ovaries. Two commonly used screening tests are transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and the CA-125 blood test. TVUS uses sound waves to visualize the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries and identify any tumors or cysts. The CA-125 blood test measures the level of a protein that may increase in women with ovarian cancer.
However, neither of these tests is definitive. A CT scan can provide detailed images of the body and help determine if cancer has spread. Ultimately, a tissue biopsy is the only method that can definitively confirm an ovarian cancer diagnosis. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample for biopsy under the guidance of a qualified ovarian cancer specialist in Ahmedabad.
Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis by an Ovarian Cancer Specialist in Ahmedabad
Ovarian cancer treatment involves various options and is often personalized based on the patient’s condition. Surgery is the most common treatment, aiming for debulking/cytoreduction, which involves removing as much of the tumor as possible. This procedure may involve removing one or both ovaries, the uterus, and potentially other tissues in the abdomen.
Fertility preserving surgical options are the treatment of choice in germ cell ovarian cancers as these cancers usually occur in young females in the reproductive age group.
Chemotherapy is another primary treatment option, administered either intravenously or directly into the abdomen. It can be used before surgery to shrink tumors or after to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Targeted therapy is a newer form of treatment that uses drugs to attack specific characteristics of cancer cells. These treatments can stop the cells from growing and dividing or cut off the blood supply to the tumors.
Hormone therapy, mainly used in certain types of ovarian cancer, uses drugs to prevent the hormones, particularly estrogen, from promoting the growth of ovarian cancer cells.
Immunotherapy is an emerging treatment option that utilizes the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It can be especially beneficial for women with advanced or recurrent ovarian cancer.
Supportive (palliative) care is also crucial, focusing on providing relief from symptoms and improving the quality of life.
Complementary methods like acupuncture, massage, and special diets are sometimes used alongside conventional treatments
Conclusion
Dr. Ridham Shah’s comprehensive approach to ovarian cancer ensures every patient receives the highest standard of care. As an Ovarian Cancer Specialist Ahmedabad, he provides personalized treatment plans that include cutting-edge surgery techniques, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and emerging immunotherapies.
His commitment extends beyond treatment, focusing on supportive care to manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. With the guidance of an experienced Ovarian Cancer Specialist Ahmedabad, patients receive a holistic approach supported by a team of specialists. Trust in Dr. Ridham’s expertise to offer hope, compassion, and exceptional medical care at every step.

Why Dr. Ridham Shah
A Surgical Oncologist Practicing In The City Of Ahmedabad
- Experience of a decade in treating cancer
- Expertise in Laparoscopic cancer surgery, Robotic cancer surgery
- Expertise in Digestive System Cancers, Colorectal cancers , Peritoneal cancers, advanced abdominal cancers
- Expertise in Cytoreductive Surgery, HIPEC, PIPAC
- Excellent support staff to help you during treatment
- 360 degree care
Specialities

Ovary Cancer

Rectal Cancer

Colon Cancer

Endometrial Cancer

Liver Cancer

Esophageal Cancer

HIPEC Surgery

Robotic Surgery

Vulvar Cancer

Gallbladder Cancer

Stomach Cancer

Pancreatic Cancer

Cervix Cancer
